Defining Bitcoin
The term Bitcoin is used to refer to a digital currency used globally and is not owned by any government; meaning the government has no authority or control over it. A person going by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto first proposed it in October 2008 in a series of technical specifications. In 2009, the Bitcoin network started operating with actual wallets and methods for transferring Bitcoins from wallet to wallet instantly over the Internet. The developer of the Bitcoin concept and initial programming code based started to dissociate himself from all future development after the year 2010. To this day no one knows exactly who the real person is behind the persona despite many attempts to identify the person.
Block Chain
The method by which Bitcoin transactions are permanently recorded in the network is conceptually referred to as a block. The blocks are stored in transaction order in a chain or a type of public general ledger. This transaction database is shared by all the nodes (wallets, etc.) interacting over the Internet based on the Bitcoin protocol. Every transaction that is executed in the currency is contained in a full copy the Bitcoin block chain. Every transaction of Bitcoin is between two addresses. These anonymous addresses are stored on the Bitcoin block chain ledger. Anyone can publically see the block chain and the full history of all transactions. You can also see the number of Bitcoins owned by any one address at any time and at any point in history.
Through a series of confirmations of transactions, every addition to the block chain is validated and confirmed. Once a new addition to the block chain has been confirmed its impossible for a transaction to be duplicated via some type of “double spend,” Double spend is the idea that a person could simultaneously send the same Bitcoins to two different addresses at the same time and thus “spend the money twice”. This helps to ensure transaction integrity and validity of the Bitcoin network.
What to keep in mind about Bitcoins
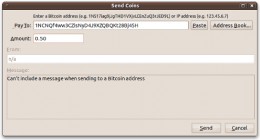
 1. The Bitcoin address
1. The Bitcoin address
A Bitcoin address simply means the unique identifier that one uses when he or she needs to receive or send Bitcoins. For example, PayPal uses an email address when one is sending funds, and so Bitcoins also need a unique identifier when sending funds which are known as the Bitcoin address. An example address would look something like this: 1JArS6jzE3AJ9sZ3aFij1BmTcpFGgN86hA.
It’s very important you are sure you have the correct Bitcoin address when sending Bitcoins to someone. Once you send the Bitcoins the transaction cannot be reversed other than to request that the receiver sends them back.
 2. The private key
2. The private key
As the name suggests, it is a secret code. A private key enables one to prove that he or she is the owner of his or her Bitcoins. Each Bitcoin address is linked up with a matching private key, normally saved in the wallet file of the Bitcoin owner. This private key is mathematically related to the Bitcoin address, making it easy for the Bitcoin address to be calculated from the private key. Make sure your private key is always kept just that… private.
 3. Charges Involved in sending Bitcoins
3. Charges Involved in sending Bitcoins
You can transact free of charge only if the total transaction is greater than 0.01 BTC. The imposed token sum of (0.0001 per 1000 bytes) is meant to provide incentives for the miners to process the transaction in the block chain. The miners refer to those individuals who run computer systems to successively calculate hashes in order to successfully create a block which earns them coins generated from the transaction fees as well as the new coins created by the blocks themselves. Currently, most transactions are typically processed in a way that involves no fee at all. A small transaction fee will be imposed for transactions involving numerous Bitcoin addresses and with a large data size. This will likely change in the future as Bitcoin becomes more popular and miners seek out profits beyond creating new Bitcoins.
 4. What ‘unconfirmed’ means?
4. What ‘unconfirmed’ means?
When you first send a Bitcoin transaction it will be unconfirmed. Only during this time can the transaction be canceled. Once it’s confirmed and placed on the block chain then it’s no longer reversible. Each transaction will be confirmed up to 6 times.
 5. What is the limit for Bitcoins generated?
5. What is the limit for Bitcoins generated?
The maximum number of Bitcoins that can be generated is 20 million. Keep in mind Bitcoin is divisible down to one Satoshi or 0.00000001.
 6. Bitcoin Clients and Wallets
6. Bitcoin Clients and Wallets
They are the base level of technology for sending and receiving Bitcoin transactions, they store the private keys required during Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin clients come in various flavors and are customized to fit in different niches. The original software written by Satoshi Nakamoto is the Bitcoin-QT Client and is downloadable at http://bitcoin.org/. It is a good option for getting started, especially for those who are not sure which client to pick. There are many other clients providing different tools and advantages. And there are also online wallets provided through companies such as coinbase.com.
Benefits of using Bitcoin and Block Chain
The Block chain is a revolutionary public ledger system that, when coupled with the Bitcoin virtual currency, provides for a powerful financial medium for virtual financial transactions. Key benefits include:
- The Bitcoin system is independent of traditional financial institutions and has extremely low processing fees and overhead.
- It is possible to transfer funds globally and anonymously.
- Bitcoins are an independent and democratic currency with no central owner.
- Bitcoins have the potential of providing more valuable benefits since it uses a digital medium.
The next few years are going to be interesting to watch as Bitcoin becomes more mainstream and the power of the block chain and low transaction costs start to disrupt the current financial environment.